Packaging down the microscope

To discuss your needs
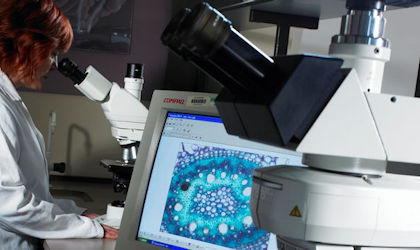
Microscopy can use a range of techniques to examine packaging materials including plastic and metal, for determination of structure, comparison against a specification and a range of packaging related problems/defects. In-depth investigation of packaging related problems/defects allows the integrity of the packaging to be investigated to see if it could have been compromised.
Plastic packaging analysis
Stereo microscopy - mainly used in the analysis of packaging defects, it allows an assessment of the defect/area of interest to help determine the next step and technique to employ.
Compound microscopy - used to view thin cryostat (frozen) sections of packaging allowing single/multiple layers to be viewed and measured, this technique can also reveal details of a defect. For example, in the case of suspected delamination this technique would confirm the presence of delamination and between which layers this had occurred.
FT-IR microscopy (with focal plane array attachment and attenuated total reflectance)- allows the identification of the polymer compositions of single and/or multi layers comprising the packaging by mapping a cross-section. The maps generated from individual areas of interest can be searched against an extensive library to identify any polymer layers.
Scanning electron microscopy (coupled with x-ray microanalysis and mapping)- used for the identification of the presence of filler materials in polymers and metallic layers which can be mapped to show the distribution of any elements of interest. This technique also allows the in-depth analysis of a defect/area of interest, for example, with suspected pin-holing in an aluminium pouch, this technique would show if the integrity of the pouch had been compromised by exposure of the aluminium.
Defects in plastic packaging can include issues such as faulty seals, delamination, perforations and pin holing. See sample report.
Metal packaging analysis
Stereo microscopy - allows an overall assessment and detailed observation of a defect/area of interest to help determine the next step and technique to employ.
Scanning electron microscopy (coupled with x-ray microanalysis and mapping)- used to identify compositions of metallic materials and in-depth analysis of a defect/area of interest. For example using a combination of x-ray microanalysis and mapping can show the presence and distribution of elements within corrosion, if high levels of chlorine are detected this may be a contributing factor to the corrosion from cooling water.
FT-IR Spectroscopy - used for the determination of lacquers which can be a contributing factor to a defect, for example internal corrosion may be caused by an incorrect lacquer being used for the type of product.
Defects associated with metal packaging can include issues such as external or internal corrosion, sulphur staining, pin holing and breaks in the lacquer/coatings. See sample report.
These tests complement a complete packaging analysis service covering all forms of packaging, using additional techniques including micro-CT scanner, dye penetration testing, pressure testing and migration testing.
For more information regarding packaging analysis please contact us.
You may also be interested in
- Laminate packaging - applications of microscopy | Summary sheet
- Foreign body identification | Video
- Identification of physical contaminants (“foreign bodies”) | White paper
- Foreign body proficiency identification scheme (FOBS) | Service
Key services

Packaging down the microscope
Microscopy use a range of techniques to examine packaging materials including plastic and metal.
Structure and physical properties
Methods for objective characterisation of food structure and physical properties.

Foreign body identification scheme
Run independently from our own foreign body laboratory, the FOBS scheme enables other laboratories to check their competence in the identification of foreign bodies.

Cereals and milling services
Cereals and milling testing services information, pricing and submission.

Meat, poultry and seafood analysis
Analysis supporting meat, poultry and seafood suppliers, manufacturers and retailers.
Packaging training courses
Explore our packaging related courses including; Packaging technology for non-packaging technologists and MAP (modified atmosphere packaging) – an introduction
Are you getting the most from your Membership?
Watch our membership FAQ videos and find out more about Member Service Account spending, Member Interest Groups, help and advice
Where we refer to UKAS Accreditation
The Campden BRI group companies listed below are accredited in accordance with the recognised International Standard ISO17025:2017 by the United Kingdom Accreditation Service (UKAS). The accreditation demonstrates technical competence for a defined scope of methods, specific to each site, as detailed in the schedules of accreditation bearing the testing laboratory number. The schedules may be revised from time to time and reissued by UKAS. The most recent issue of the schedules are available from the UKAS website www.ukas.com. Campden BRI (Chipping Campden) Limited is a UKAS accredited testing laboratory No. 1079






